Ever wonder how AI does it's magic? Find out in 2mins.
Remember the thrill of discovering simple math functions in school? What if I told you that the same concept could unlock the mysteries of AI? Join me as we demystify AI together!
The Problem
Here's the thing: Most people feel like AI is magic or complex. They envision complex algorithms, enormous datasets, and high-level math reserved for experts. It's easy to feel lost and think the incredible capabilities of AI are beyond your grasp. Why can't it be simpler? Why can't we break it down to something as straightforward as basic math concept we learned in school? The good news is, we can – let’s tackle that intimidating facade together and make it relatable and approachable.
Why It Matters
Understanding a simple math concept can unlock your understanding of how AI works. Relating the intricacies of AI to something as elementary as a linear equation transcends the barrier of complexity, making AI more accessible and less intimidating. It empowers you to engage more meaningfully with AI technologies. Suddenly, you realize that the magical veil of AI is just a sophisticated extension of concepts you already grasp.
This realization can spark curiosity and confidence, propelling you to explore more advanced facets of AI without hesitation. Equipped with this knowledge, you're no longer just a passive observer of AI advancements; instead, you actively appreciate and contribute to the dialogue around this transformative technology.
The Solution
So, how do we solve the problem of demystifying AI? Remember plotting graphs in school where 'x' was along the bottom and 'y' was vertical? The equation of a straight line, y = ax + b, is foundational, and guess what? AI models, at their core, use similar concepts.

Language Models 101
AI language models guess the next word in a sentence. You give it a sentence, and it predicts the next word, repeating the process until it's unsure.
Preparing the Data
To create a language model, you need training data. Imagine an Excel file with two columns: user input (text) and AI output (text). This data is converted into numbers, as math works better with numbers than letters.
Plotting the Points
The numbers from the text are plotted on a graph, resulting in a scatter plot with many points.
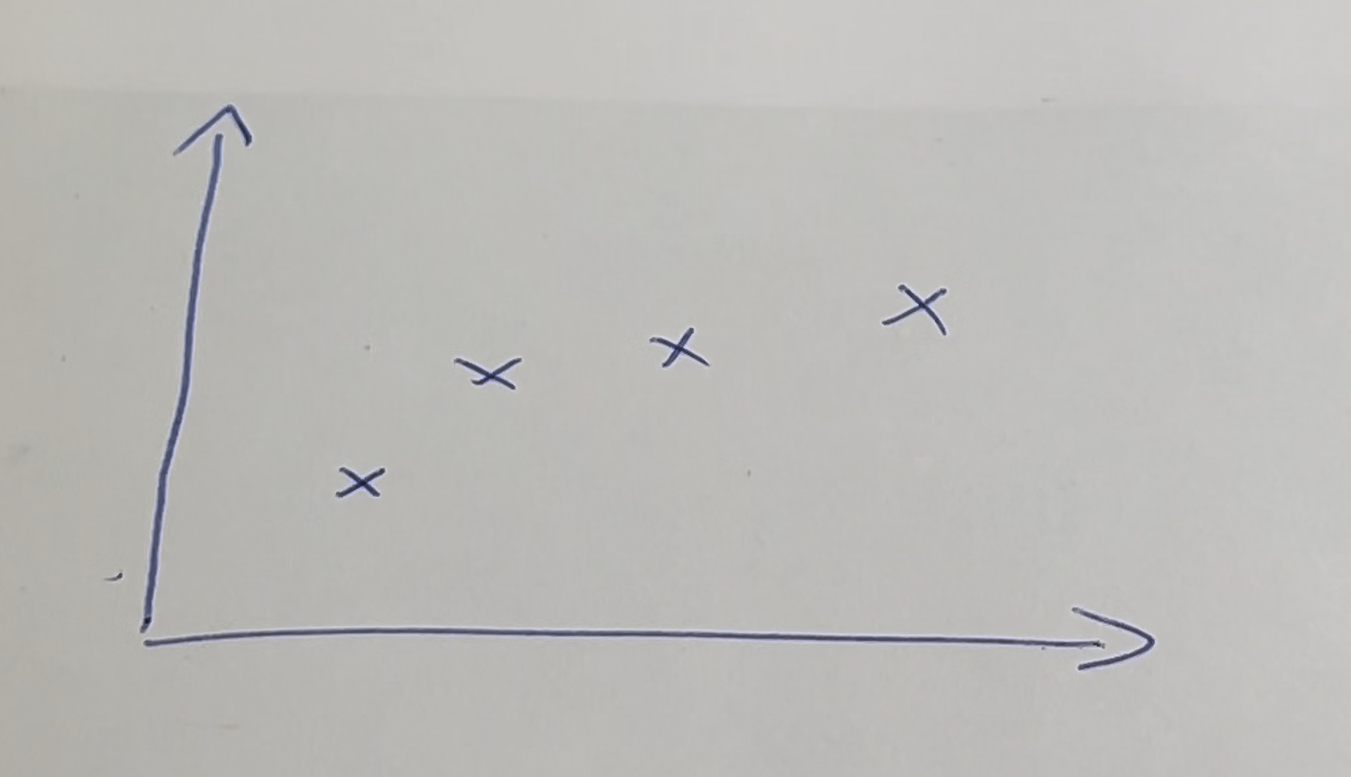

Training the Model
The AI tries to find the find a line that covers the most amount of points, testing various options until it finds a good match. This process is called training.
How it Works
Once trained, the model can predict output text based on input text, just like solving for y in y = ax + b. You put a value for "x" in there and you know what y is. Where "x" is the text you type, and y is the AI's best guess at what you want to see. For example, we have y = 2x + 1, if x=1, then y = 2*1+1 = 3
The principle remains the same in AI, even though the actual equation is more complex (y = ax + by + cz + ...), imagine going from the 2D in the images above to 3D, 4D,...million D. That's when our brain cannot think about it, but the concept is the same.
What can you do with this information?
- Lift the mystic cloud of AI: Understanding AI's basics dispels the mystery surrounding this technology, empowering you to approach it with confidence.
- Recognize AI's limitations: You'll understand that AI, like any other tool, can make mistakes. It may provide incorrect answers or struggle with tasks that require human intuition or creativity.
- Engage in meaningful conversations: Share your newfound knowledge with others, discussing AI's potential and limitations, and encouraging responsible development and use.
- Explore AI applications: With a solid foundation in AI concepts, you can explore various AI-powered tools and services, leveraging their capabilities to enhance your work or personal projects.
- Stay informed and adapt: As AI evolves, your understanding of its basics will enable you to stay informed about the latest developments and adapt to new technologies and innovations.
- Participate in shaping AI's future: By understanding AI's fundamentals, you can contribute to the ongoing discussion about AI's ethical and societal implications, helping to ensure that AI is developed and used responsibly.
And feel free to share the article with your network if you found it useful.
Conclusion
Ready to unlock the potential of AI with this foundational knowledge? Join AI Juicing now and start your journey into the fascinating world of AI, equipped with insights that make complex concepts crystal clear! 🚀